The dawn of a new era in astronomy has begun as the world gets its first look at the full capabilities of NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope, a partnership with ESA (European Space Agency) and CSA (Canadian Space Agency). The telescope’s first full-color images and spectroscopic data were released during a televised broadcast at 8:00 PM IST (14:30 UTC) on Tuesday, July 12, 2022, from NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Maryland. These listed targets below represent the first wave of full-color scientific images and spectra the observatory has gathered, and the official beginning of Webb’s general science operations. They were selected by an international committee of representatives from NASA, ESA, CSA, and the Space Telescope Science Institute.
These first images from the world’s largest and most powerful space telescope demonstrate Webb at its full power, ready to begin its mission to unfold the infrared universe.
SMACS 0723
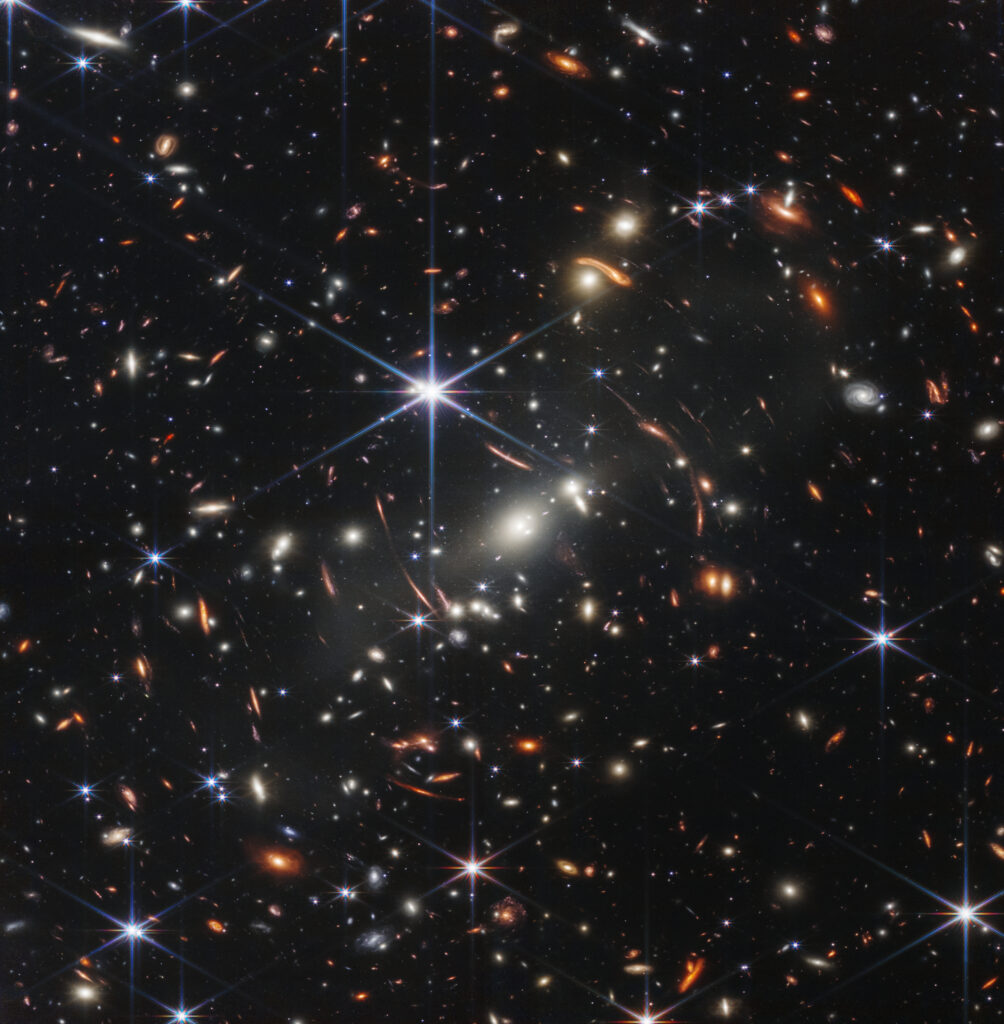

NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope has produced the deepest and sharpest infrared image of the distant universe to date. Known as Webb’s First Deep Field, this image of galaxy cluster SMACS 0723 is overflowing with detail.
Thousands of galaxies – including the faintest objects ever observed in the infrared – have appeared in Webb’s view for the first time. This slice of the vast universe covers a patch of sky approximately the size of a grain of sand held at arm’s length by someone on the ground.
- Learn more about this image
- Download the full-resolution, uncompressed version and supporting visuals from the Space Telescope Science Institute
WASP-96 b
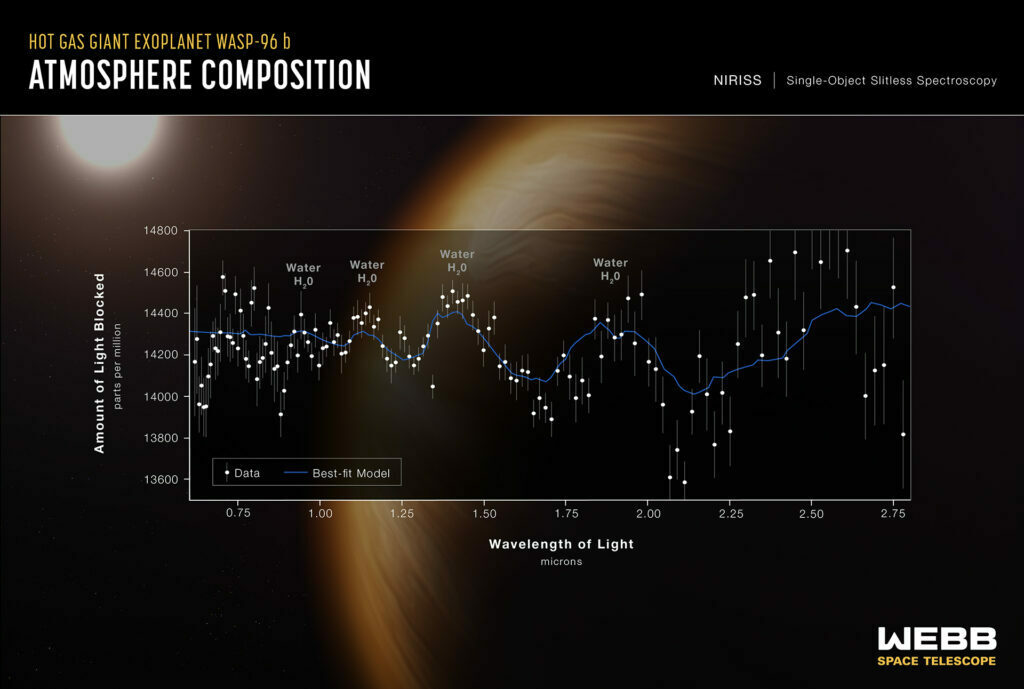
NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope has captured the distinct signature of water, along with evidence for clouds and haze, in the atmosphere surrounding a hot, puffy gas giant planet orbiting a distant Sun-like star.
The observation, which reveals the presence of specific gas molecules based on tiny decreases in the brightness of precise colors of light, is the most detailed of its kind to date, demonstrating Webb’s unprecedented ability to analyze atmospheres hundreds of light-years away.
While the Hubble Space Telescope has analyzed numerous exoplanet atmospheres over the past two decades, capturing the first clear detection of water in 2013, Webb’s immediate and more detailed observation marks a giant leap forward in the quest to characterize potentially habitable planets beyond Earth.
- Learn more about this image
- Download the full-resolution, uncompressed version and supporting visuals from the Space Telescope Science Institute
Southern Ring Nebula
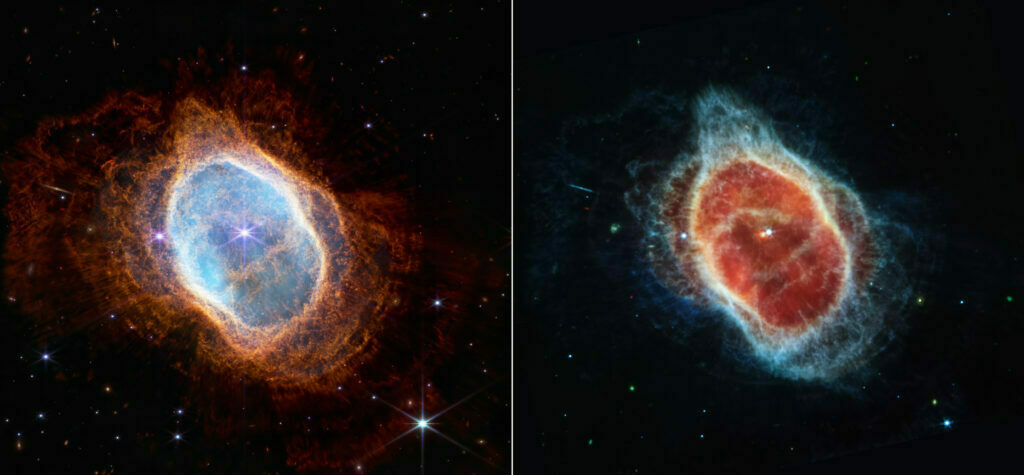

Some stars save the best for last.
The dimmer star at the center of this scene has been sending out rings of gas and dust for thousands of years in all directions, and NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope has revealed for the first time that this star is cloaked in dust.
Two cameras aboard Webb captured the latest image of this planetary nebula, cataloged as NGC 3132, and known informally as the Southern Ring Nebula. It is approximately 2,500 light-years away.
Webb will allow astronomers to dig into many more specifics about planetary nebulae like this one – clouds of gas and dust expelled by dying stars. Understanding which molecules are present, and where they lie throughout the shells of gas and dust will help researchers refine their knowledge of these objects.
- Learn more about this image
- Download the full-resolution, uncompressed version and supporting visuals from the Space Telescope Science Institute
- View a Hubble Space Telescope image of the Southern Ring Nebula
Stephan’s Quintet
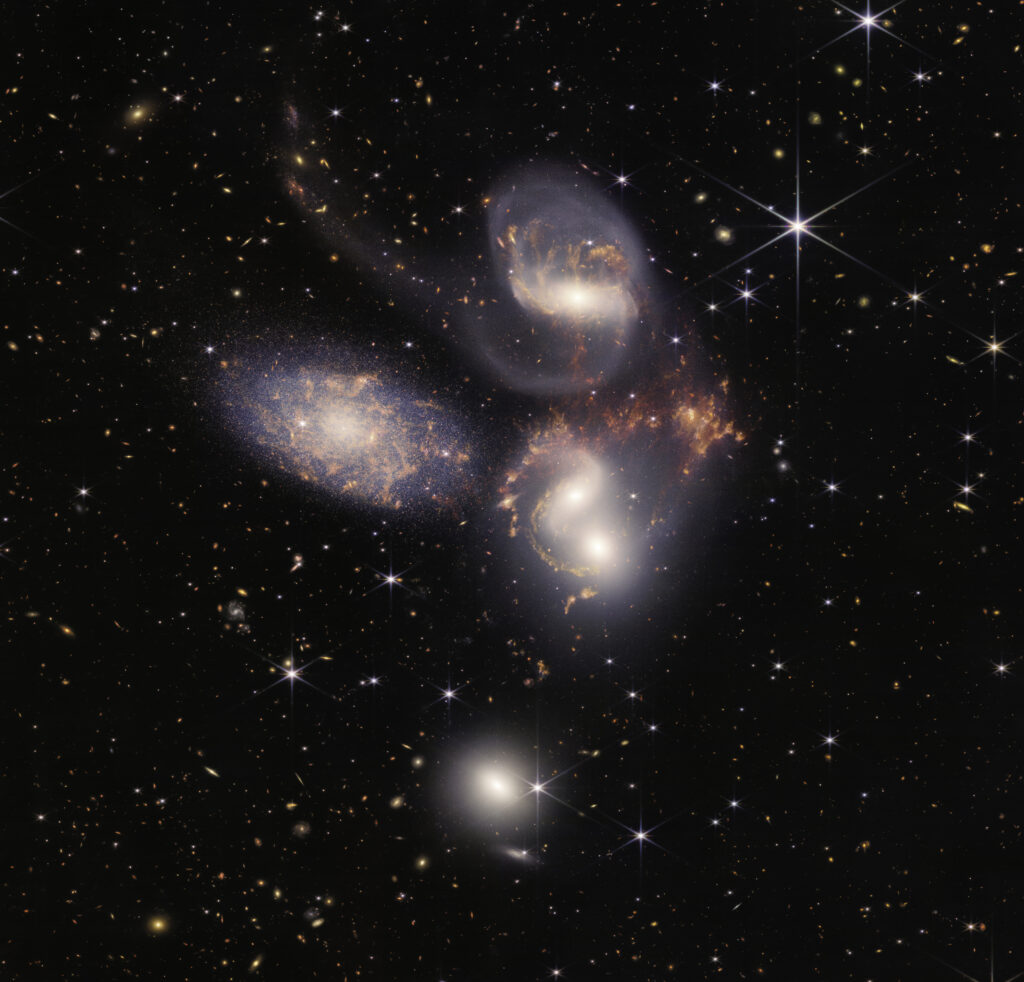

Stephan’s Quintet, a visual grouping of five galaxies, is best known for being prominently featured in the holiday classic film, “It’s a Wonderful Life.” Today, NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope reveals Stephan’s Quintet in a new light. This enormous mosaic is Webb’s largest image to date, covering about one-fifth of the Moon’s diameter. It contains over 150 million pixels and is constructed from almost 1,000 separate image files. The information from Webb provides new insights into how galactic interactions may have driven galaxy evolution in the early universe.
With its powerful, infrared vision and extremely high spatial resolution, Webb shows never-before-seen details in this galaxy group. Sparkling clusters of millions of young stars and starburst regions of fresh star birth grace the image. Sweeping tails of gas, dust and stars are being pulled from several of the galaxies due to gravitational interactions. Most dramatically, Webb captures huge shock waves as one of the galaxies, NGC 7318B, smashes through the cluster.
- Learn more about this image
- Download the full-resolution, uncompressed version and supporting visuals from the Space Telescope Science Institute
- View a Hubble Space Telescope image of Stephan’s Quintet (ESAHubble.org)
Carina Nebula
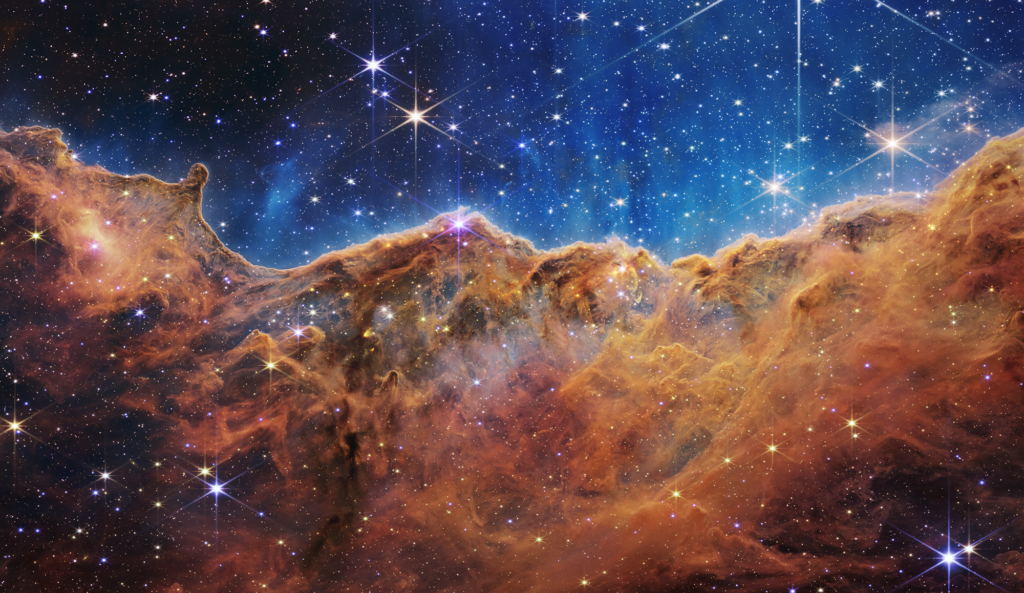

This landscape of “mountains” and “valleys” speckled with glittering stars is actually the edge of a nearby, young, star-forming region called NGC 3324 in the Carina Nebula. Captured in infrared light by NASA’s new James Webb Space Telescope, this image reveals for the first time previously invisible areas of star birth.
Called the Cosmic Cliffs, Webb’s seemingly three-dimensional picture looks like craggy mountains on a moonlit evening. In reality, it is the edge of the giant, gaseous cavity within NGC 3324, and the tallest “peaks” in this image are about 7 light-years high. The cavernous area has been carved from the nebula by the intense ultraviolet radiation and stellar winds from extremely massive, hot, young stars located in the center of the bubble, above the area shown in this image.
- Learn more about this image
- Download the full-resolution, uncompressed version and supporting visuals from the Space Telescope Science Institute
- View a Hubble Space Telescope image of Carina Nebula NGC 3324 (Hubblesite.org)
The James Webb Space Telescope is the world’s premier space science observatory. Webb will solve mysteries in our solar system, look beyond to distant worlds around other stars, and probe the mysterious structures and origins of our universe and our place in it. Webb is an international program led by NASA with its partners, ESA (European Space Agency) and CSA (Canadian Space Agency).
NASA Headquarters oversees the mission for the agency’s Science Mission Directorate. NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Maryland, manages Webb for the agency and oversees work on the mission performed by the Space Telescope Science Institute, Northrop Grumman, and other mission partners. In addition to Goddard, several NASA centers contributed to the project, including the agency’s Johnson Space Center in Houston; Jet Propulsion Laboratory (JPL) in Southern California; Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama; Ames Research Center in California’s Silicon Valley; and others.
NIRCam was built by a team at the University of Arizona and Lockheed Martin’s Advanced Technology Center.
MIRI was contributed by ESA and NASA, with the instrument designed and built by a consortium of nationally funded European Institutes (The MIRI European Consortium) in partnership with JPL and the University of Arizona.
Download full-resolution, uncompressed versions and supporting visuals for this image from the Space Telescope Science Institute: https://webbtelescope.org/contents/news-releases/2022/news-2022-031
Image Credits: NASA, ESA, CSA, and STScI
Track James Webb Space Telescope Launch HERE
